Dr. Matthew Wielicki: The Weather Stations We Never Had
How sparse thermometers and generous infilling built a global temperature story.
A central pillar of the climate-crisis narrative is simple enough to fit on a bumper sticker… today is the hottest in human history. That line only works if you accept, without question, that we have reliable, global temperature data before satellites. We do not. What we have is a patchwork of land stations concentrated in a few developed regions, a lot of ocean guesses from ship tracks, and then, later, generous statistical infilling.
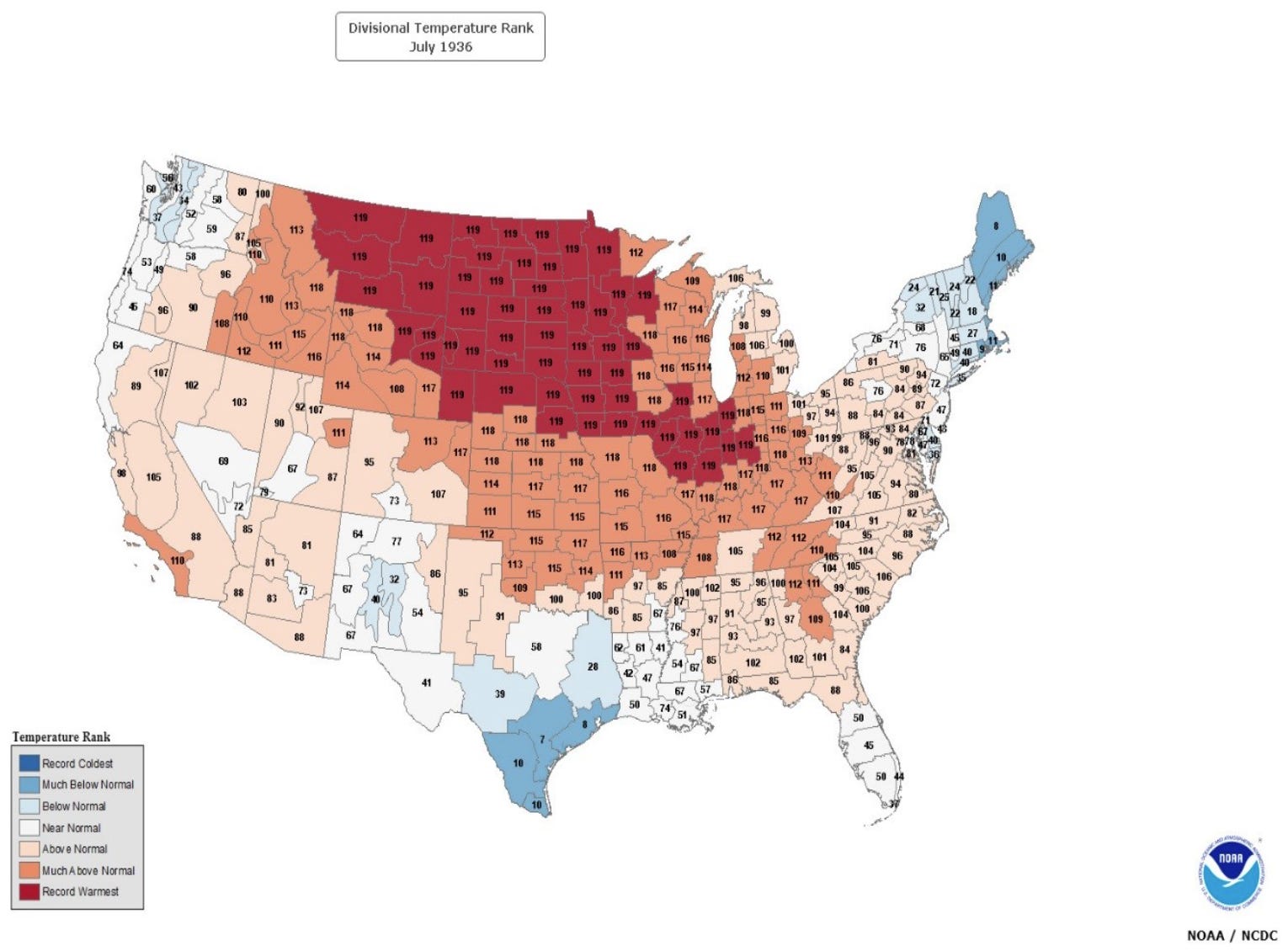
Everyone agrees the 1930s were brutally hot across the United States… the Dust Bowl was a humanitarian and ecological disaster. Crops failed, soils blew away, and heat waves killed thousands. NOAA’s own retrospectives still call out 1936 as a benchmark summer, and July 1936 remains a singular month in the U.S. record.
Atmospheric CO₂ at that time was roughly 310 PPM, a level derived from ice core records and widely used in NASA’s GISS datasets.
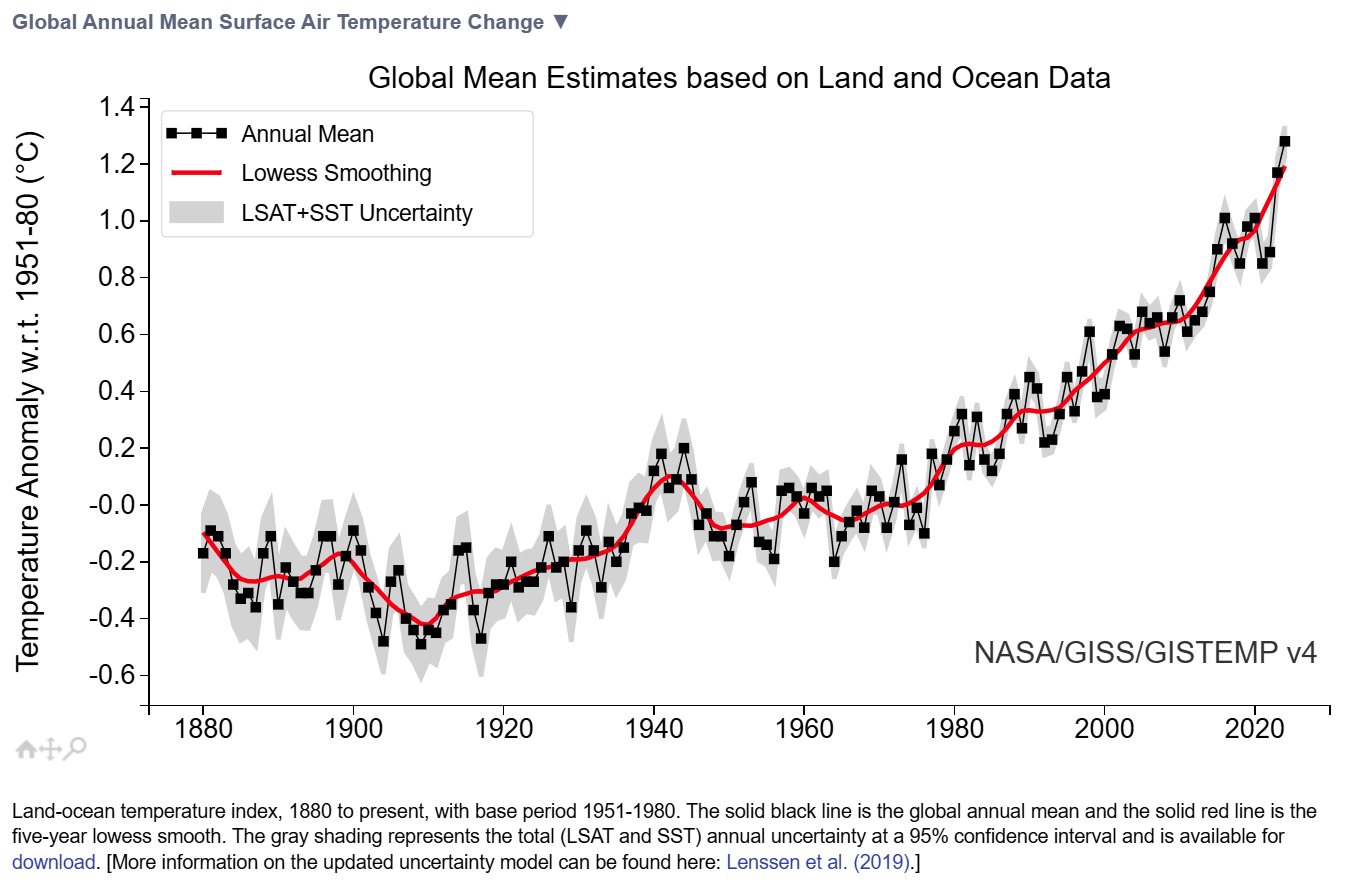
So the story we are told goes like this… yes, the U.S. was scorched in the 1930s, but the world was cooler, and only in the modern era did global temperatures rise everywhere. That story depends less on observations and more on algorithms.
The global map we never measured
Now the uncomfortable part. When there are no thermometers, you either leave grid boxes blank, or you paint numbers in from far away. HadCRUT historically left many boxes blank, explicitly avoiding interpolation, which means the “global” mean depends on where you have observations. NASA’s GISTEMP goes the other direction and spreads anomalies up to twelve hundred kilometers from a station, filling the gaps with 1200 km smoothing. Those are not trivial choices, they are the ballgame.
If you overlay the 1930s anomaly map with the station density maps, you see something obvious… warm where the thermometers were numerous, cool or neutral where coverage was threadbare. A compilation of historical station distribution between 1921 and 1950 makes the same basic point… the network was sparse and badly unbalanced.
Today’s “records,” the jet-exhaust problem
If you want to read more you have to subscribe to Irrational Fear

Dr. Matthew Wielicki
This article was published on 9 August 2025 by Dr Matthew Wielicki on his website Irrational Fear.
By subscribing you can unlock the full breakdown, plus get access to more than 380 deep-dive pieces that dismantle the pillars of the climate crisis narrative.
more news
The Polar Bear Narrative: What Scientists Knew Before Frozen Planet Aired
In 2011, BBC viewers were told that polar bears in the Barents Sea were starving due to climate-driven sea ice loss. Later scientific evidence shows that this portrayal was inconsistent with data already available at the time.
Why Is the Southern Ocean Cooling? Three New Scientific Explanations Challenge Climate Models
Surface temperatures in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica have cooled for decades, defying the projections of leading climate models and puzzling researchers worldwide. In this article, physicist Ralph B. Alexander examines three recent studies that propose strikingly different explanations for this unexpected climate anomaly.
Utility Scale Lithium Based Energy Storage Systems
Large-scale lithium-ion battery storage is expanding rapidly, often with limited public discussion of safety and environmental risks. The article below examines a recent white paper by engineer Richard Ellenbogen that analyzes these risks, particularly when such facilities are sited in densely populated or environmentally sensitive areas.