Right, New York Times, Scientists Do Disagree on The Polar Vortex
A recent New York Times article explores claims that climate change may be worsening winter cold extremes. While some scientists argue that Arctic warming destabilizes the polar vortex, long-term data show a clear decline in extreme cold events, challenging that narrative.
A recent article in The New York Times (NYT) “What’s Up With This Big Freeze? Some Scientists See Climate Change Link” describes different perspectives of climate scientists regarding winter cold extremes. Some scientists are claiming based on climate model projections that global warming is making extreme cold snaps worse, others point out that that data does not support those claims. The latter are correct, long-term trend data points towards a clear decline in extreme cold rather than any increase in polar breakouts.
Saying this perspective is held by only “some scientists” is a step in the right direction for the NYT. It is certainly a more honest take than last week’s firm declaration that “climate change is fueling extremes, both hot and cold,” which Climate Realism debunked with well established weather data.
NYT reports that at least one scientist, Dr. Cohen from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, says “climate warming in the Arctic is causing this disruption of the polar vortex,” which leads to breakouts of extreme cold from the Arctic, brought south by the polar jet stream.
The polar vortex theory is unfounded in historical evidence. The theory isn’t new, climate alarmists have fearmongered about a “destabilizing” polar jet stream for years, and data has long existed that refutes it. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration wrote after a February 2021 cold snap that “on average, winters are warmer and cold extremes are less likely than they were a century ago.”
Climate Realism has covered the polar vortex/jet stream issue several times, here, here, and here, and the evidence has not become stronger since those posts.
The NYT recovered a modicum of credibility by acknowledging a handful of other perspectives, saying “not all scientists agree.” The authors quote other expert research scientists saying the models and papers published by Cohen and his collaborators are “often not that convincing,” because “long-term temperature trends and climate models show the exact opposite[.]”
Another scientist interviewed explained “[w]hat the data shows is that these cold extremes are getting less extreme, and they will continue to get less extreme,” and “it’s difficult to link a given weather event, such as a cold spell, to climate change.”
All of this is absolutely true.
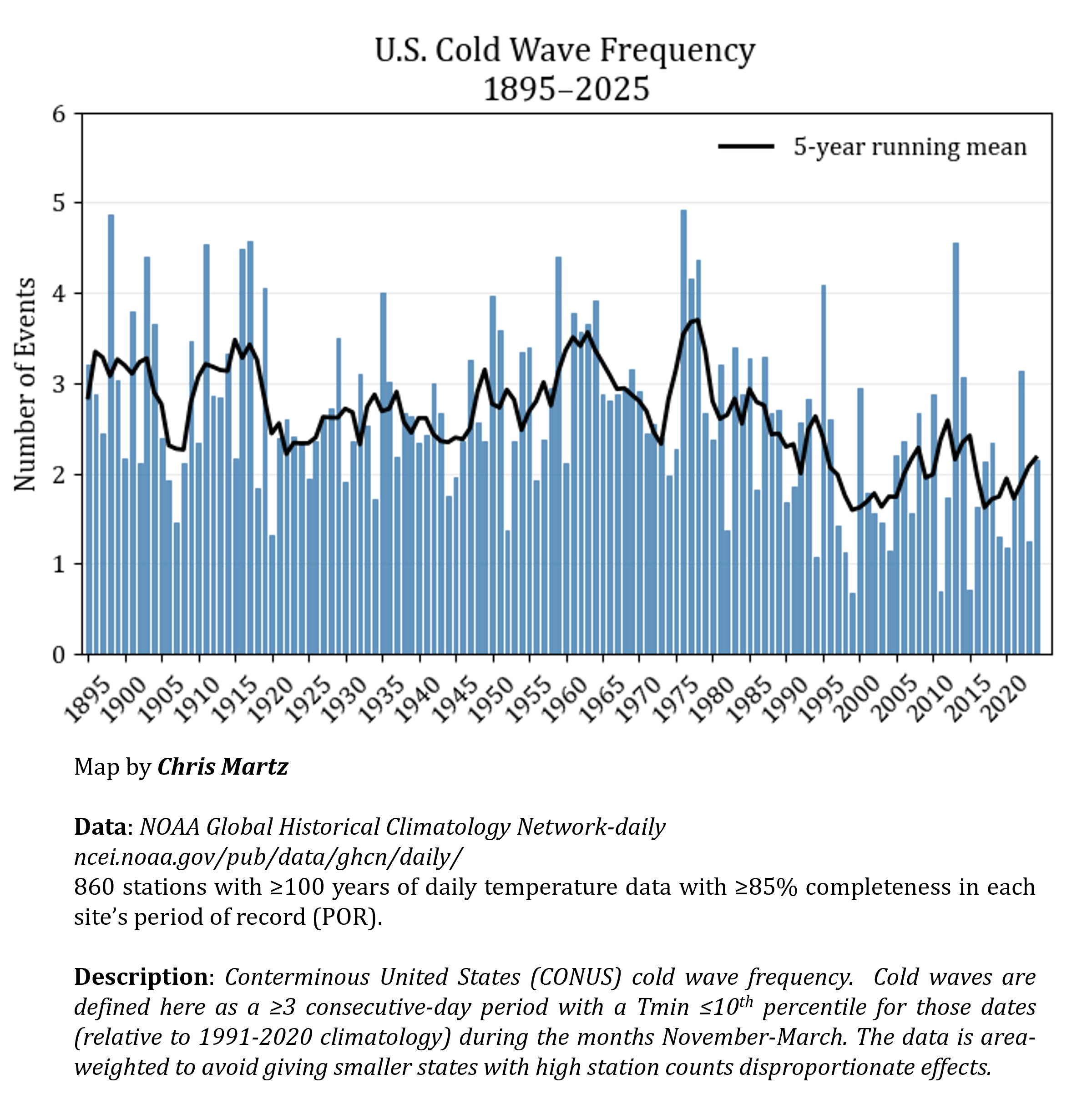
Publicly available data looking at deadly cold snaps in the United States show they are becoming less frequent over time, not more. Winters in the 1890s, 1910s, and 1970s were significantly worse than they are today. (See figure below)
If climate change was causing more polar vortex instability, we would not see a trend towards fewer cold extremes.
Where the NYT fails in this article is where they insist with no nuance that “warming has been largely driven by the burning of oil, gas and coal.”
Alarmists say this like a mantra in just about every article that touches on the weather or climate issues, and it’s just as unverified as the claims that the NYT cited asserting that climate change is making the polar vortex less stable. There is no legitimate scientific consensus that the modest warming of the past century is either largely driven by fossil fuel use or threatens catastrophic consequences.
There is a lot of debate and nuance with regard to these issues that The New York Times’ readers would probably benefit from hearing about, if only the paper would provide balanced coverage of the issue, as it did in this article on the polar vortex and cold weather.
more news
Interview with Dr. Guus Berkhout: A Different Perspective on Climate Science and Energy Policy
The big problem today is that climate models are not fit-for-purpose, says Clintel co-founder dr. Guus Berkhout. They do not reflect the real world. That is the reason why the Net Zero policy does not work. We need fundamental changes in climate science and climate policies. We now see that this message gets more and more support.
Judge Rejects Climate Dogma, Begins to Restore Integrity
In a significant move for scientific accountability, a U.S. federal judge has removed a controversial climate change chapter from a key judicial reference manual. The decision challenges the dominance of model-based climate narratives in the courts and signals a renewed emphasis on empirical evidence and institutional integrity.
Ed Miliband is the last fool standing on Net Zero
As the United States moves to reconsider key climate regulations, Britain’s aggressive push toward Net Zero is drawing increasing scrutiny. In this commentary, Matt Ridley argues that unilateral decarbonisation risks leaving the UK economically isolated while much of the world shifts course.