COP30 Is Lying To Justify Its Existence
COP30 is building its case on climate misinformation that rewrites the past to claim a victory it never earned.
The COP30 agreement claims the world was previously on track for more than 4C of warming until the Paris Agreement heroically “bent” that trajectory down to 2.3–2.5C:
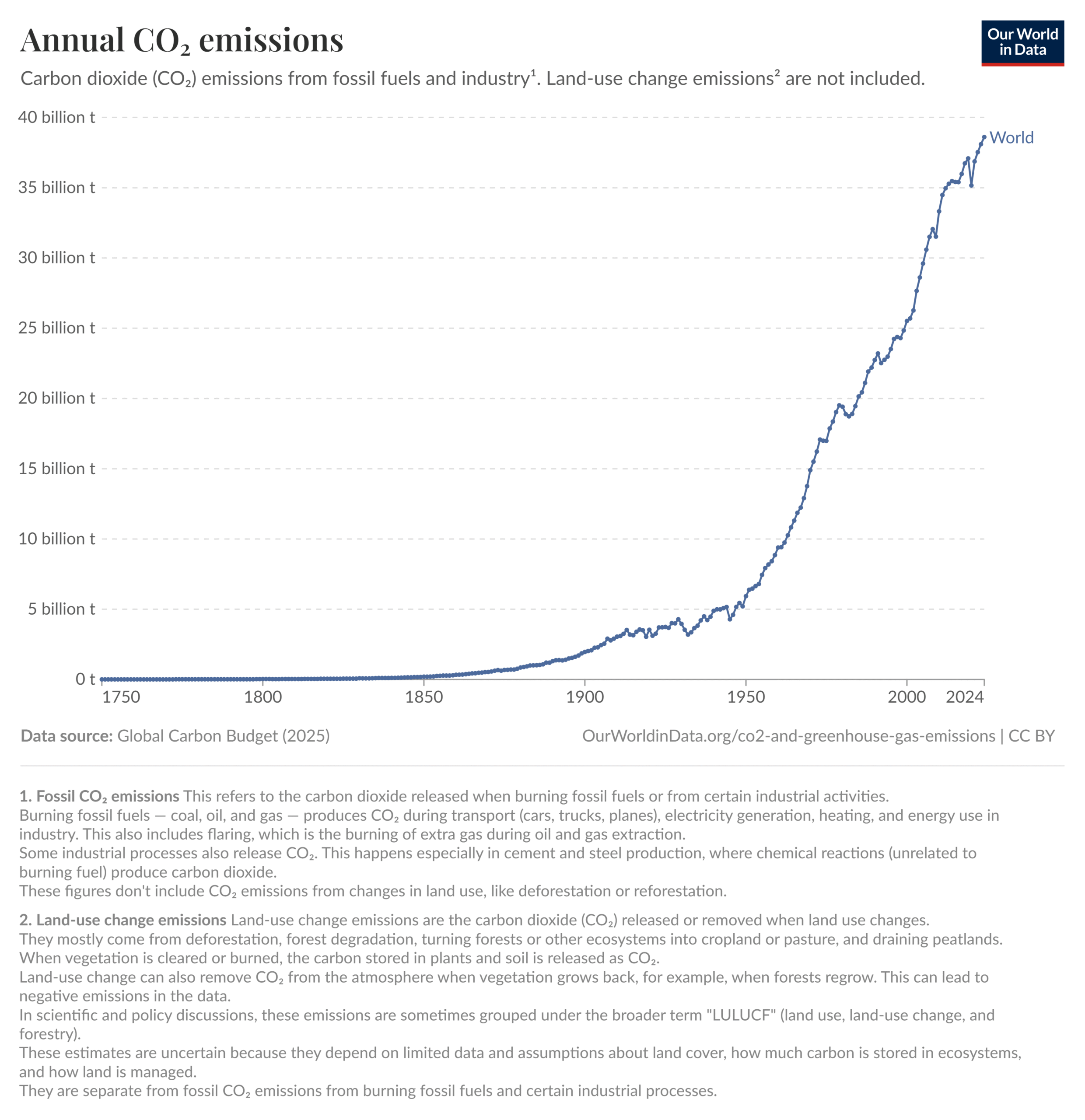
However, “this is misinformation,” says Roger Pielke Jr., Professor of Environmental Studies at the University of Colorado Boulder. It is a fiction built on the carcass of RCP8.5 — the extreme scenario that scientists quietly abandoned years ago because it required impossible coal use, implausible demographics and an economic collapse that never happened.
COP30 is resurrecting an unrealistic, disowned scenario in order to claim that Paris saved the world. The problem is the data. Real-world emissions show no curve bending, no slowdown and no “Paris effect”.
Paris didn’t change emissions, but it did unlock a permanent justification for climate taxation, energy rationing and the dismantling of cheap, reliable power — the foundation of economic prosperity.
COP30 needs a victory to justify its existence. So it has rewritten history: invent a 4C trajectory, pretend Paris knocked it down, and congratulate itself for saving humanity.
The world was never heading for RCP8.5. Paris didn’t change emissions.
Lies.
more news
A review of The Frozen Climate Views of the IPCC, part 2
Clintel has analyzed IPCC’s Assessment Report 6 (AR6) and has published an important report on it, entitled: The Frozen Climate Views of the IPCC. It’s a report that provides many serious criticisms of the work carried out by the IPCC. Here you find the second and last part of a review of this important work by Clintel, recently published by the French website Climat et Vérité.
Javier Vinós on the Hunga Tonga Eruption and its extraordinary Climate Effects
In a recent ICSF/Clintel lecture, Dr. Javier Vinós argued that the January 15, 2022 Hunga Tonga eruption was the main cause of the extraordinary global climate anomalies of 2023–2024. He describes them as the first genuine multi-year global climate event in roughly 80 years, widely misinterpreted by mainstream analyses.
Swiss television tries to refute climate sceptics and fails
The editorial team of the Swiss weather program SRF Meteo has attempted to expose ‘arguments of climate sceptics’ as false. However, what they present as the alleged ‘state of science’ does not stand up to fact-checking.